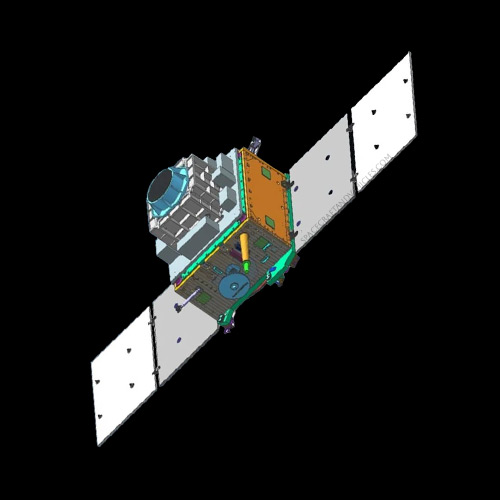
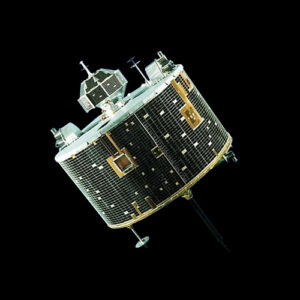
XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite) is an Indian space mission designed to study the polarization of X-rays emitted by celestial objects. Launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), XPoSat aims to unravel the mysteries surrounding high-energy phenomena in the universe, including black holes, neutron stars, and active galactic nuclei.
The significance of the XPoSat program lies in its unique capability to measure the polarization of X-rays, providing insights into the magnetic fields and geometry of cosmic sources. Notable achievements include XPoSat’s successful deployment and its contributions to advancing our understanding of the universe’s most energetic processes.
Design and Construction
XPoSat features a compact and lightweight design optimized for space-based X-ray polarimetry. The spacecraft’s structure is constructed using advanced composite materials to minimize weight while ensuring structural integrity in the harsh space environment.
Unique engineering challenges during its development included designing sensitive X-ray polarimeters capable of measuring polarization signals with high precision. Engineers overcame these challenges through innovative design solutions and rigorous testing to ensure XPoSat’s scientific accuracy and reliability.
Mission Objectives
XPoSat’s primary mission objectives are to:
- Measure the polarization of X-rays emitted by various celestial sources, including black holes, neutron stars, and active galactic nuclei.
- Investigate the magnetic fields and geometry of X-ray emitting regions in cosmic objects.
- Study the mechanisms responsible for X-ray emission and polarization in different astrophysical environments.
Launch and Deployment
XPoSat was launched aboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India. The launch took place on [insert launch date]. The deployment of XPoSat into its designated orbit was successful, enabling the spacecraft to begin its scientific observations. Key discoveries and findings during the mission include the detection of polarized X-ray emission from black hole accretion disks and neutron star magnetospheres.
Technical Specifications
- Payload Capacity: XPoSat carries specialized X-ray polarimeters capable of detecting polarization signals from celestial objects.
- Propulsion System: XPoSat utilizes reaction control thrusters for orbital maneuvers and attitude control.
- Power Source: The spacecraft is powered by solar panels, providing electrical power for its scientific instruments and subsystems.
Current Status
As of 2024, XPoSat remains active in orbit, conducting scientific observations and contributing to ongoing research in X-ray astronomy. Its data continues to be analyzed by scientists worldwide, leading to new discoveries and advancements in our understanding of the universe’s high-energy phenomena.