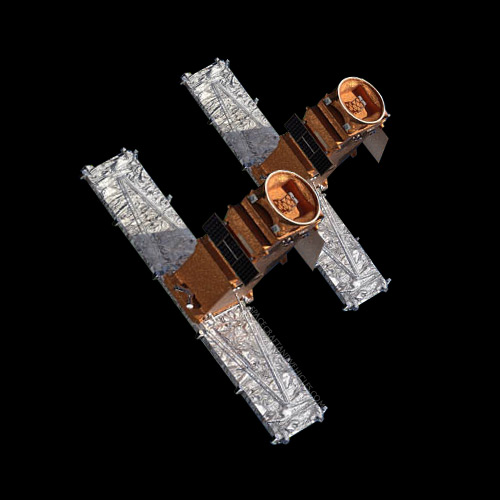
The RADARSAT Constellation is a trio of Earth observation satellites developed by the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) to provide comprehensive and frequent monitoring of Canada’s land and waters, as well as the Arctic, maritime approaches, and resource development. Launched in June 2019, this constellation marks a significant milestone in Canadian space technology, offering improved imaging capabilities and enhanced data continuity for applications such as environmental monitoring, disaster management, and maritime surveillance.
Design and Construction
The RADARSAT Constellation satellites feature a modular design with a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) payload optimized for all-weather, day-and-night imaging. Constructed primarily of lightweight materials to minimize launch mass, each satellite is equipped with deployable solar panels for power generation and high-gain antennas for data transmission. Unique engineering challenges included designing the satellites to operate in tandem, coordinating data collection and transmission among the three spacecraft while maintaining precise orbital alignment.
Mission Objectives
The primary mission objective of the RADARSAT Constellation is to provide continuous, high-resolution radar imagery for a variety of applications, including ice monitoring, disaster management, agricultural monitoring, and environmental surveillance. Secondary objectives include supporting maritime surveillance, resource development, and infrastructure monitoring, contributing to Canada’s national security and sovereignty.
Launch and Deployment
The RADARSAT Constellation was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, in June 2019. Deployment occurred successfully, with each satellite being released into its designated orbit. Since then, the constellation has been operational, capturing and transmitting SAR imagery for various applications. Notable milestones include the acquisition and delivery of imagery for emergency response efforts during natural disasters.
Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: Approximately 3.6 meters in length, 1.2 meters in diameter
- Weight: Each satellite weighs approximately 1,420 kilograms
- Payload Capacity: Equipped with a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) payload
- Propulsion System: Utilizes onboard thrusters for orbit maintenance
- Power Source: Solar panels for power generation
- Instruments and Equipment: SAR payload for imaging with various imaging modes and polarization options
Current Status
As of 2024, the RADARSAT Constellation is active and operational, providing valuable Earth observation data to various stakeholders in Canada and around the world. The satellites continue to support ongoing missions related to environmental monitoring, disaster management, and national security. Additionally, plans for future enhancements and upgrades to the constellation may be underway to further improve its capabilities.