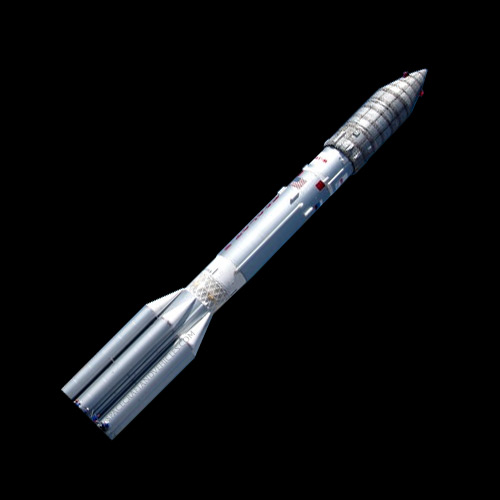
The Proton rocket family stands as one of the most iconic and reliable launch vehicles in the history of space exploration. Developed by the Russian space agency, Roscosmos, the Proton rockets have been instrumental in launching a wide array of payloads, including satellites, space probes, and modules for space stations. Notable for their robustness and versatility, Proton rockets have played a significant role in advancing space exploration and satellite deployment, making them a cornerstone of the global space industry.
Design and Construction
Proton rockets feature a three-stage design consisting of a first stage powered by liquid oxygen (LOX) and refined kerosene (RP-1) engines, followed by a second stage and a third stage powered by liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen engines.
The rocket’s construction primarily utilizes lightweight yet durable materials such as aluminum alloys and composite structures to maximize payload capacity. Unique engineering challenges overcome during its development include optimizing engine performance, ensuring structural integrity, and addressing complex aerodynamic considerations.
Mission Objectives
The primary mission objectives of the Proton rocket family include launching satellites and payloads into various orbits, including geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) and low Earth orbit (LEO). Additionally, Proton rockets have been used to deploy interplanetary probes, space station modules, and components for manned space missions. Secondary objectives encompass supporting international collaborations, commercial satellite launches, and advancing Russia’s space exploration capabilities.
Launch and Deployment
Proton rockets have been launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, with the first launch dating back to July 1965. While the Proton family has achieved numerous successful launches, it has encountered occasional setbacks, including launch failures and anomalies during deployment. However, key milestones include the launch of the first module of the International Space Station (ISS) and the deployment of critical components for Russia’s space program.
Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: Height: Approximately 58 meters
- Weight: Approximately 700,000 kilograms
- Payload Capacity: Up to 22,000 kilograms to low Earth orbit (LEO)
- Propulsion System: Liquid oxygen (LOX) and refined kerosene (RP-1) engines
- Power Source: N/A (Rocket itself is not powered)
- Instruments and Equipment: N/A (Designed for payload delivery)
Current Status
As of 2024, the Proton rocket family remains active, continuing to serve as a reliable workhorse for satellite launches and space exploration missions. While newer launch vehicles have emerged, Proton rockets continue to be utilized for a variety of missions, including commercial satellite launches and international collaborations. Future plans may involve upgrades and modernizations to enhance the Proton’s capabilities and maintain its competitiveness in the global space market.