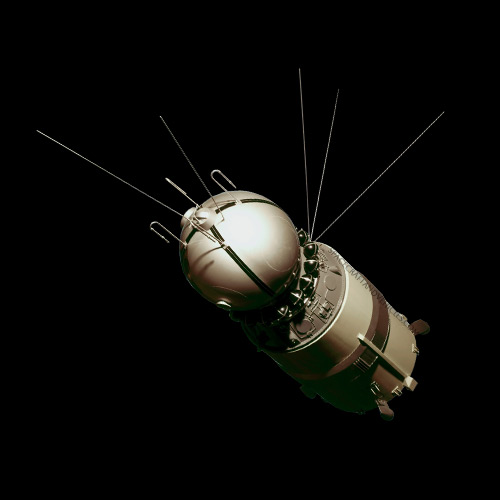
The Zenit satellites, developed by the Soviet Union and later Russia, played a crucial role in reconnaissance and intelligence gathering during the Cold War and beyond. Notable for their advanced imaging capabilities, these satellites provided vital information for military and strategic purposes, contributing to the space race era.
Design and Construction
The Zenit satellites featured a robust design optimized for reconnaissance missions, incorporating high-resolution cameras and sophisticated imaging systems. Constructed from lightweight yet durable materials, they were equipped with advanced avionics and propulsion systems to ensure precise maneuverability in orbit. Overcoming challenges in designing compact yet powerful imaging instruments and maintaining operational stability were key aspects of their development.
Mission Objectives
The primary mission objective of the Zenit satellites was to conduct reconnaissance and intelligence-gathering operations, including monitoring military installations, strategic targets, and potential threats. Secondary objectives included scientific research, technological experimentation, and international collaboration.
Launch and Deployment
The Zenit satellites were typically launched atop dedicated rockets, including the Zenit and R-7 series, from various launch sites across the Soviet Union and later Russia. They were deployed into various orbits, depending on the specific mission requirements. Despite occasional issues during launch and deployment, these satellites achieved numerous significant milestones and provided invaluable intelligence data.
Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: Varied depending on the specific Zenit model.
- Weight: Typically several tons.
- Payload Capacity: Equipped with high-resolution cameras and imaging systems.
- Propulsion System: Utilized onboard propulsion for orbit adjustments and maneuvers.
- Power Source: Solar panels provided electrical power.
- Instruments and Equipment: Advanced imaging instruments, telemetry systems, and communication equipment.
Current Status
As of 2024, most Zenit satellites have been retired from active service, replaced by newer reconnaissance satellites with enhanced capabilities. However, their legacy continues to influence modern satellite design and intelligence-gathering strategies. Russia may have future plans for satellite development and reconnaissance missions.