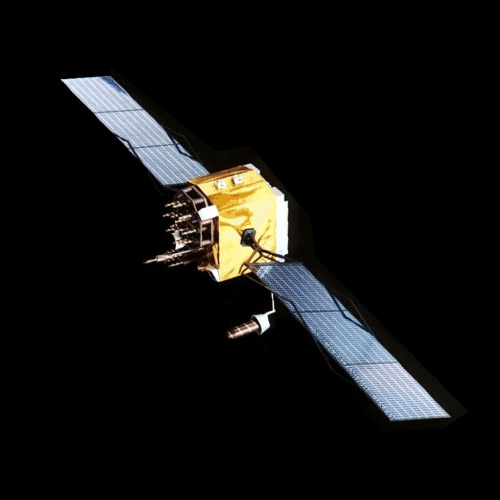
AstroSat is India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory satellite, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on September 28, 2015. Its primary purpose is to observe celestial objects across the electromagnetic spectrum, including ultraviolet, optical, and X-ray wavelengths.
The AstroSat Program holds significant importance as it enhances India’s capabilities in space-based astronomy and contributes valuable data to international scientific research efforts. Notable achievements include its successful deployment and the groundbreaking discoveries it has facilitated, revolutionizing our understanding of the universe’s high-energy phenomena.
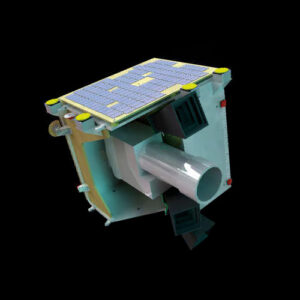
Design and Construction
AstroSat features a modular design, with a main satellite bus housing the spacecraft’s subsystems and scientific instruments. It is constructed using lightweight materials to optimize its mass and ensure efficient operation in space. The spacecraft’s unique engineering challenges included designing sensitive scientific instruments capable of observing celestial objects across multiple wavelengths and integrating them into a single satellite platform. Engineers overcame these challenges through meticulous testing and calibration to ensure AstroSat’s scientific accuracy and reliability.
Mission Objectives
AstroSat’s primary mission objectives are to:
- Conduct multi-wavelength observations of celestial sources to study their properties and behavior.
- Investigate transient and variable phenomena in the universe, such as supernovae, gamma-ray bursts, and active galactic nuclei.
- Study the composition, structure, and dynamics of various astronomical objects, including stars, galaxies, and galaxy clusters.
Launch and Deployment
AstroSat was launched aboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C30) from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India, on September 28, 2015. The launch was successful, and AstroSat was deployed into a near-Earth orbit. Since then, the spacecraft has conducted numerous scientific observations, leading to significant discoveries, including the detection of X-ray emissions from distant black holes and neutron stars.
Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: Approximately 3.6 meters in length and 1.5 meters in diameter.
- Weight: Approximately 1,513 kilograms.
- Payload Capacity: AstroSat carries five scientific instruments, including ultraviolet and X-ray telescopes, capable of observing celestial objects across multiple wavelengths.
- Propulsion System: AstroSat is equipped with reaction control thrusters for orbital maneuvers and attitude control.
- Power Source: The spacecraft is powered by solar panels, providing electrical power for its scientific instruments and subsystems.
Current Status
As of 2024, AstroSat remains active in orbit, conducting scientific observations and contributing to ongoing research in astronomy and astrophysics. Its data continues to be analyzed by scientists worldwide, leading to new discoveries and insights into the universe’s mysteries.