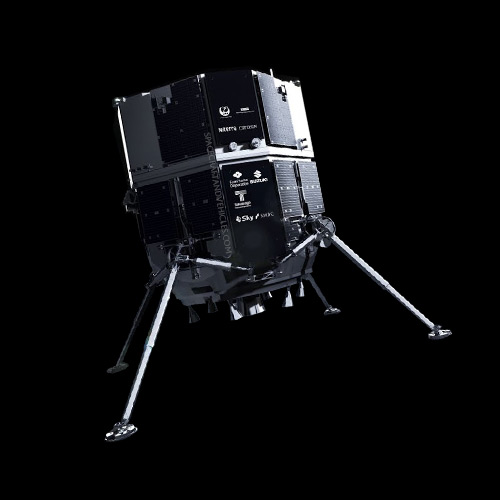
The Hakuto-R spacecraft, developed by ispace Inc., represents a pioneering effort in private lunar exploration. As part of the Google Lunar XPRIZE competition, Hakuto-R aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of small robotic rovers for lunar exploration and to foster commercial space activities. Notable for its innovative approach, Hakuto-R sought to explore the lunar surface, conduct scientific experiments, and inspire the next generation of space explorers.
Design and Construction
Hakuto-R featured a compact and lightweight design optimized for mobility on the lunar surface. It comprised a rover equipped with scientific instruments for surface analysis, communication systems for data transmission, and solar panels for power generation. Constructed using advanced materials and engineering techniques, the rover prioritized durability and reliability in the challenging lunar environment. Unique engineering challenges included designing a rover capable of navigating rugged terrain, surviving extreme temperature variations, and withstanding lunar dust.
Mission Objectives
The primary mission objective of Hakuto-R was to explore the lunar surface, conducting scientific experiments and capturing high-resolution images to study geological features. Secondary objectives included testing technologies for future lunar missions, demonstrating the capabilities of private space exploration initiatives, and inspiring global interest in lunar exploration.
Launch and Deployment
Hakuto-R was intended to be launched aboard a commercial lunar lander, such as Astrobotic’s Peregrine lander, for deployment on the Moon’s surface. However, due to delays in the Google Lunar XPRIZE competition timeline and changes in ispace Inc.’s lunar exploration strategy, Hakuto-R’s launch and deployment plans were revised. As of the latest information available, Hakuto-R has not yet been deployed to the lunar surface.
Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: Approximately 1.5 meters in length, 1 meter in width, and 0.5 meters in height
- Weight: Approximately 20 kilograms
- Payload Capacity: Scientific instruments for surface analysis and imaging
- Propulsion: Electric motors for mobility on the lunar surface
- Power Source: Solar panels generating up to 200 watts of power
- Instruments and Equipment: Cameras, spectrometers, and other scientific instruments for lunar surface exploration.
Current Status
As of 2024, Hakuto-R’s current status is uncertain, as it has not yet been deployed to the lunar surface. However, ispace Inc. continues to pursue its lunar exploration ambitions through its “Hakuto” program, which includes plans for future lunar missions and the development of commercial lunar exploration services.