The Space Shuttle, a groundbreaking spacecraft developed by NASA, revolutionized human spaceflight and exploration. Introduced in the 1980s, the Space Shuttle program aimed to provide a reusable and versatile means of transporting astronauts and cargo to and from low Earth orbit. With its iconic orbiter, solid rocket boosters, and external fuel tank, the Space Shuttle became a symbol of American ingenuity and ambition in space. Over three decades of service, the Space Shuttle fleet facilitated numerous missions.
Design and Construction
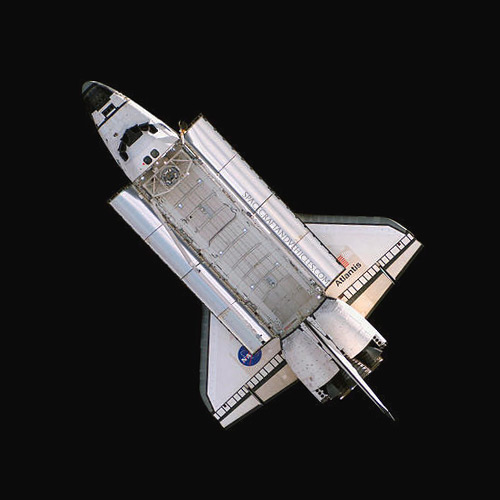
The Space Shuttle spacecraft consisted of three major components: the orbiter, solid rocket boosters (SRBs), and external fuel tank (ET). The orbiter, resembling a traditional aircraft, housed the crew cabin, payload bay, and main engines. Constructed from lightweight yet durable materials such as aluminum and reinforced carbon-carbon, the orbiter was designed for multiple missions and reentries into Earth’s atmosphere.
The SRBs provided additional thrust during liftoff and ascent, each containing solid rocket propellant and thrust vector control systems. The ET, located between the SRBs, held the liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellants for the orbiter’s main engines. Together, these components formed the Space Shuttle stack, allowing for controlled ascent into orbit and subsequent separation of the orbiter for mission objectives.
Mission Objectives
- The primary objective of the Space Shuttle program was to provide routine access to space for crewed missions, satellite deployment, and space station assembly.
- Secondary objectives included scientific research, technology demonstration, and international collaboration in space exploration.
Launch and Deployment
- Space Shuttle missions were launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida atop the Space Transportation System (STS), comprising the orbiter, SRBs, and ET.
- After reaching orbit, the orbiter deployed satellites, conducted experiments, and performed rendezvous and docking maneuvers with other spacecraft.
Design and Construction
NASA’s Space Shuttle program featured five iconic orbiters that played a pivotal role in advancing human space exploration: Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour. Each shuttle had its own unique story and contributions, helping NASA achieve milestones in science, engineering, and international cooperation.
Space Shuttle Columbia
Columbia was the first operational shuttle, making its debut flight in 1981 with STS-1, the first-ever reusable spacecraft to go to orbit. Columbia conducted pioneering missions, including the deployment of satellites and research experiments, but tragically disintegrated during reentry in 2003 on STS-107, leading to the loss of its crew.

Space Shuttle Challenger
Challenger, the second orbiter, launched in 1983 and quickly became a workhorse for NASA. It was the first shuttle to carry a woman, Sally Ride, and achieved several other milestones, including hosting the first spacewalk using a jetpack. Challenger’s career ended in disaster in 1986 when it broke apart shortly after liftoff on STS-51-L, leading to major reforms in NASA’s safety protocols.

Space Shuttle Discovery
Discovery, the third shuttle, holds the record for the most missions: 39 over 27 years. It was a part of historic achievements like deploying the Hubble Space Telescope and helping to assemble the International Space Station (ISS). Discovery also returned to flight after both the Challenger and Columbia disasters, symbolizing NASA’s resilience.
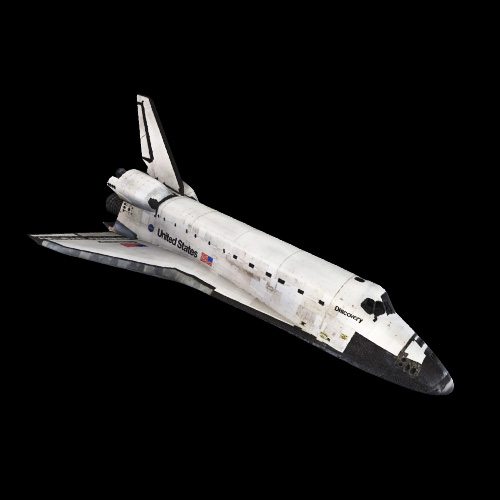

Space Shuttle Atlantis
Atlantis, the fourth orbiter, became famous for its diverse missions, including deploying the Galileo spacecraft to Jupiter and docking with the Russian space station Mir. Atlantis also supported many ISS construction missions and carried out the final servicing mission to the Hubble Telescope. Its last flight, STS-135 in 2011, marked the end of the Space Shuttle program.

Space Shuttle Endeavour
Endeavour, the youngest in the fleet, was built to replace Challenger. It launched for the first time in 1992 and carried out critical missions like the first servicing of the Hubble Telescope and delivering key components to the ISS. Endeavour’s final mission in 2011 left a lasting legacy of collaboration and innovation.

Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: The Space Shuttle orbiter measured approximately XX meters in length and XX meters in wingspan, with a payload bay capable of accommodating large payloads.
- Weight: The orbiter had a launch mass of approximately XX,XXX kilograms, including payloads and crew.
- Power Source: The orbiter was powered by three main engines fueled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, while the SRBs provided additional thrust during liftoff.
Current Status
The Space Shuttle program concluded in 2011 after 135 missions spanning over three decades of service. Despite its achievements, including the deployment of satellites, construction of the ISS, and advancement of space technology, the Space Shuttle fleet was retired to make way for future exploration initiatives.
Following the retirement of the Space Shuttle, NASA transitioned to new launch vehicles and spacecraft, including the Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft, for crewed missions beyond low Earth orbit. The legacy of the Space Shuttle program continues to inspire future generations of space explorers and serves as a testament to human perseverance and innovation in the pursuit of knowledge beyond Earth.