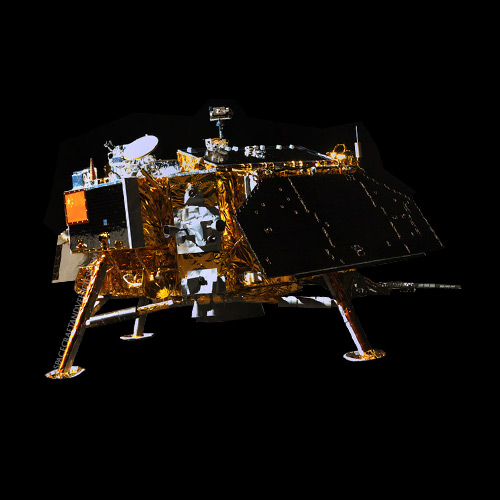
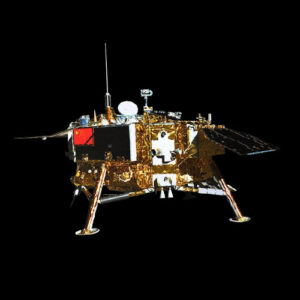
The Chang’e 3 Lunar Lander marked a significant milestone in China’s space exploration program, becoming the first Chinese spacecraft to achieve a soft landing on the Moon. Its primary purpose was to conduct scientific research and exploration of the lunar surface, contributing to humanity’s understanding of Earth’s natural satellite.
Design and Construction
The Chang’e 3 Lunar Lander featured a robust design equipped with scientific instruments to analyze the lunar environment. Constructed primarily of lightweight materials, it incorporated landing gear and solar panels to ensure stable operation on the lunar surface. Engineering challenges included designing a propulsion system capable of achieving a soft landing and surviving the harsh lunar conditions.
Mission Objectives
The primary objective of the Chang’e 3 Lunar Lander was to conduct in-situ exploration of the lunar surface. This included deploying the Yutu rover to explore the surrounding area and conducting scientific experiments to study the lunar geology, atmosphere, and space environment.
Launch and Deployment
The Chang’e 3 Lunar Lander was launched aboard a Long March 3B rocket from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center on December 1, 2013. It successfully landed on the Moon’s surface in the Sinus Iridum region on December 14, 2013. The deployment of the Yutu rover marked a significant achievement for China’s space program.
Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: Approximately 3.6 meters tall and 2 meters wide.
- Weight: Approximately 1,200 kilograms.
- Propulsion: Landing propulsion system for soft landing.
- Power Source: Solar panels for power generation.
- Instruments and Equipment: Cameras, spectrometers, and other scientific instruments for lunar surface analysis.
Current Status
The Chang’e 3 Lunar Lander successfully completed its primary mission and operated on the lunar surface for over two years. It ceased functioning in March 2015 but remains a significant achievement in China’s space exploration history.